Tiras Johnson, age 23, was unarmed when he was shot and killed in Tulsa, Oklahoma. His family was devastated by his death, and they were struggling to pay for Tiras’ funeral. Like many victims’ families, Tiras’ mother applied for financial compensation through the Oklahoma Crime Victims Compensation Act in order to cover his funeral costs, but instead received a surprising response in the mail.
The letter, addressed to Tiras’ mother, Netarsha, explained that her claim was ineligible for funds because of implied contributory conduct -- that is, that the incident “appeared to be gang-related” and “[Tiras] exercised poor judgment by choosing to be a gang member.” All compensation was denied. “We extend our condolences for the loss of your loved one,” it read.
Tiras wasn’t a gang member, for the record, but of far greater importance is that he played no contributory role in his own death. As it turns out, he would be one of many Black victims often denied compensation for the very same crimes as committed against white victims, who did receive compensation.
The Oklahoma Crime Victims Compensation Act is intended to fairly compensate victims, or their surviving families, for expenses incurred “as a result of the criminal acts of other persons.” Eligibility requirements for receiving funds include the existence of sufficient evidence that the compensation wouldn’t benefit the offender (e.g., in a domestic violence case), that the crime was reported within a specified amount of time, and that the victim was not complicit in the crime (which includes the arbitrary rule that one must not be associated with a gang). The fund is managed by the District Attorneys Council, and claims are approved or denied in each District Attorney’s office. Unfortunately, there is evidence to suggest that these eligibility requirements are not applied equally to Black and white victims and their families.
The ACLU Analytics team analyzed data from the District Attorneys Counsel, which oversees the program, to understand if our suspicions about disparate compensation were true. The data included information about the demographics (including race), crime, claims, and claim results of each victim that applied for compensation between late 2008 and early 2019. Sadly, the results were even worse than we expected.
Controlling for type of crime, crime location, and amount of monetary compensation requested, Black victims were 1.6 times more likely to be denied funds entirely than white victims. Further, Black male victims were almost 2 times more likely than white female victims to be denied monetary compensation.
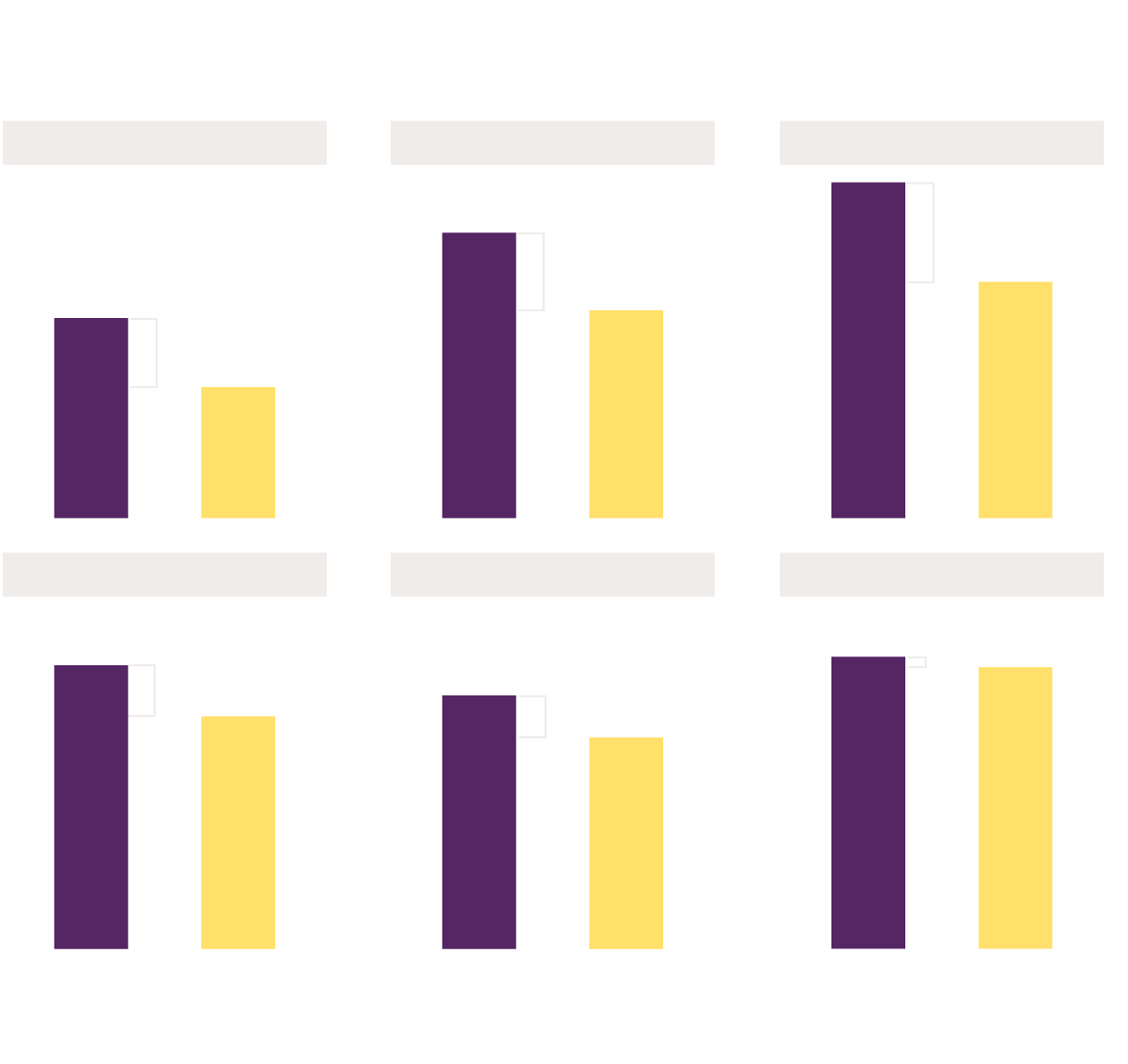
Black Victims of Same Crimes Denied Funds More Often
Denial rates for Black and white victims for each crime category
SHOOTING W/ INTENT TO KILL
CHILD ABUSE
HOMICIDE
44% of Black victims of
homicide were denied funds
compared to 29% of white
victims of homicide
22 pps
17 pps
Denied 15 pct.
74%
points more
63%
52%
46%
44%
29%
OTHER
SEXUAL ASSAULT
ASSAULT
3 pps
12 pps
9 pps
65%
63%
62%
56%
51%
47%
Black Victims
White Victims
Black
White
Black
White
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or “withdrawn” statuses were eliminated from analysis.
25 offense types were grouped into 6 crime categories in this graph.
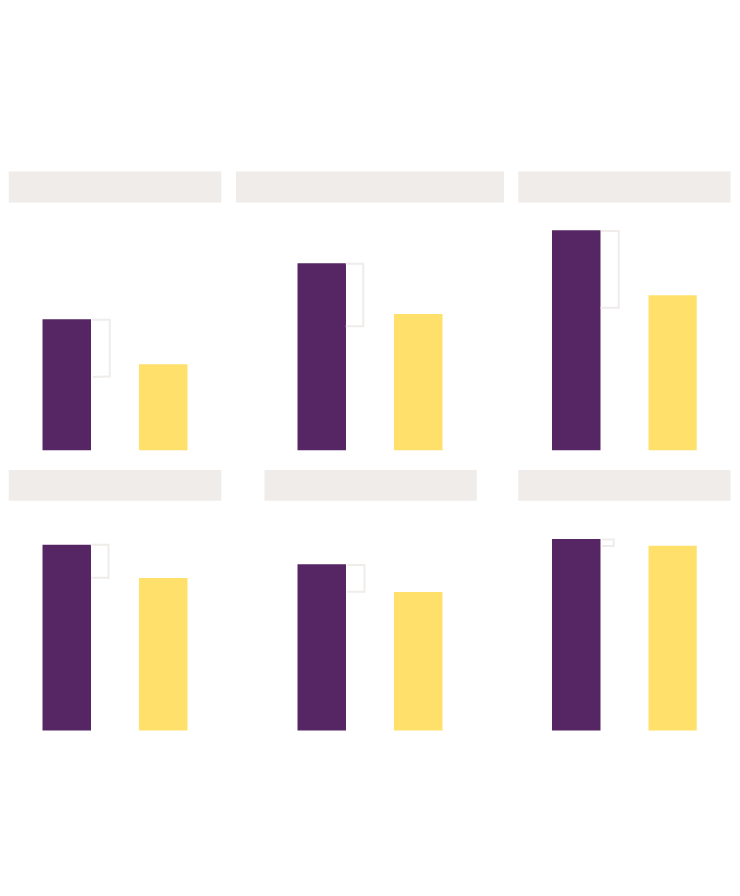

Black Victims of Same Crimes Denied
Funds More Often
Denial rates for Black and white victims of each crime
SHOOTING - INTENT TO KILL
CHILD ABUSE
HOMICIDE
44% of Black victims of
homicide were denied
funds compared to 29% of
white victims of homicide
22 pps
17 pps
Denied 15 pct,
74%
points more
63%
52%
46%
44%
29%
OTHER
SEXUAL ASSAULT
ASSAULT
3 pps
12 pps
9 pps
65%
63%
62%
56%
51%
47%
Black
Victims
White
Victims
Black
White
Black
White
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or “withdrawn”
statuses were eliminated from analysis. 25 offense types were grouped
into 6 crime categories in this graph.
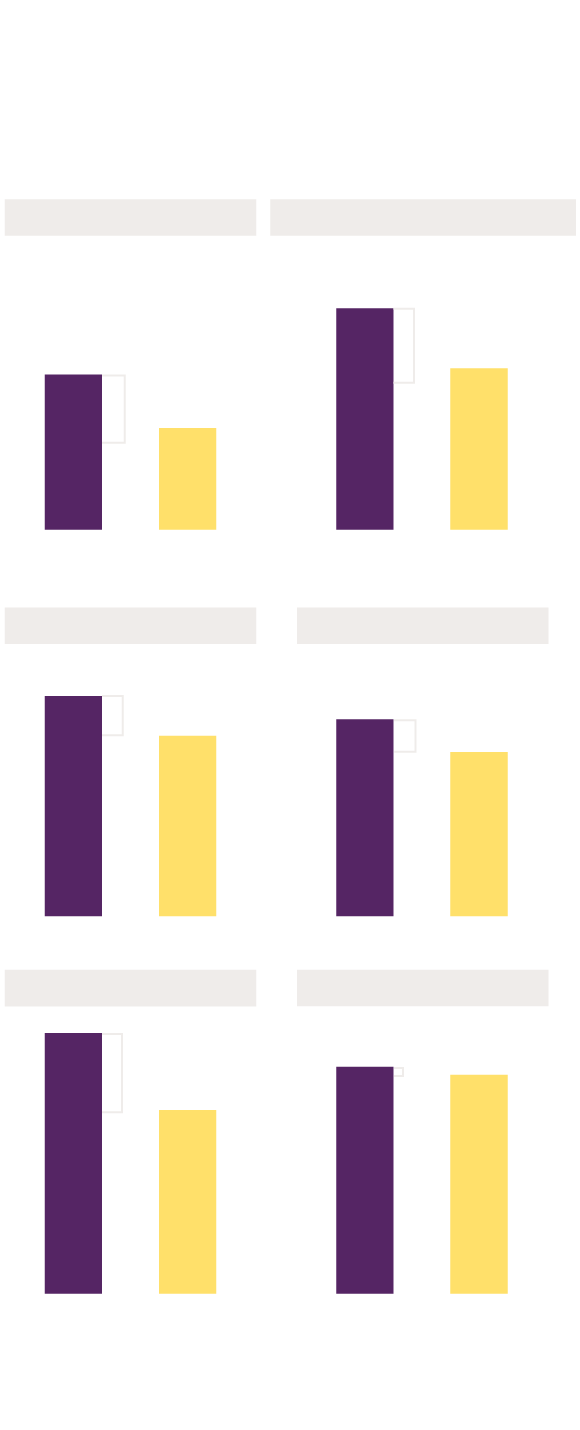
Black Victims of Same Crimes
Denied Funds More Often
Denial rates for Black and white victims
of each crime category
SHOOTING - INTENT TO KILL
HOMICIDE
44% of Black victims of
homicide were denied
funds compared to 29%
of white victims of homicide
17 pps
Denied 15 pct.
points more
63%
46%
44%
29%
Black
Victims
White
Victims
White
Black
SEXUAL ASSAULT
ASSAULT
12 pps
9 pps
63%
56%
51%
47%
Black
White
Black
White
CHILD ABUSE
OTHER
3 pps
22 pps
74%
65%
62%
52%
Black
White
Black
White
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or
“withdrawn” statuses were eliminated from analysis. 25 offense
types were grouped into 6 crime categories in this graph.
Black people were disproportionately victims of serious crimes, but especially unlikely to receive compensation. Of just over 2,300 Black victims represented in the dataset with “denied” or “awarded” judgments, over 42% were victims of homicide or shootings with intent to kill. This is compared to just 17% of the nearly 7,250 white victims that requested compensation. Black people were being shot and killed at almost 2.5X the rate of white people, yet being denied compensatory funds more often for their deaths and suffering.
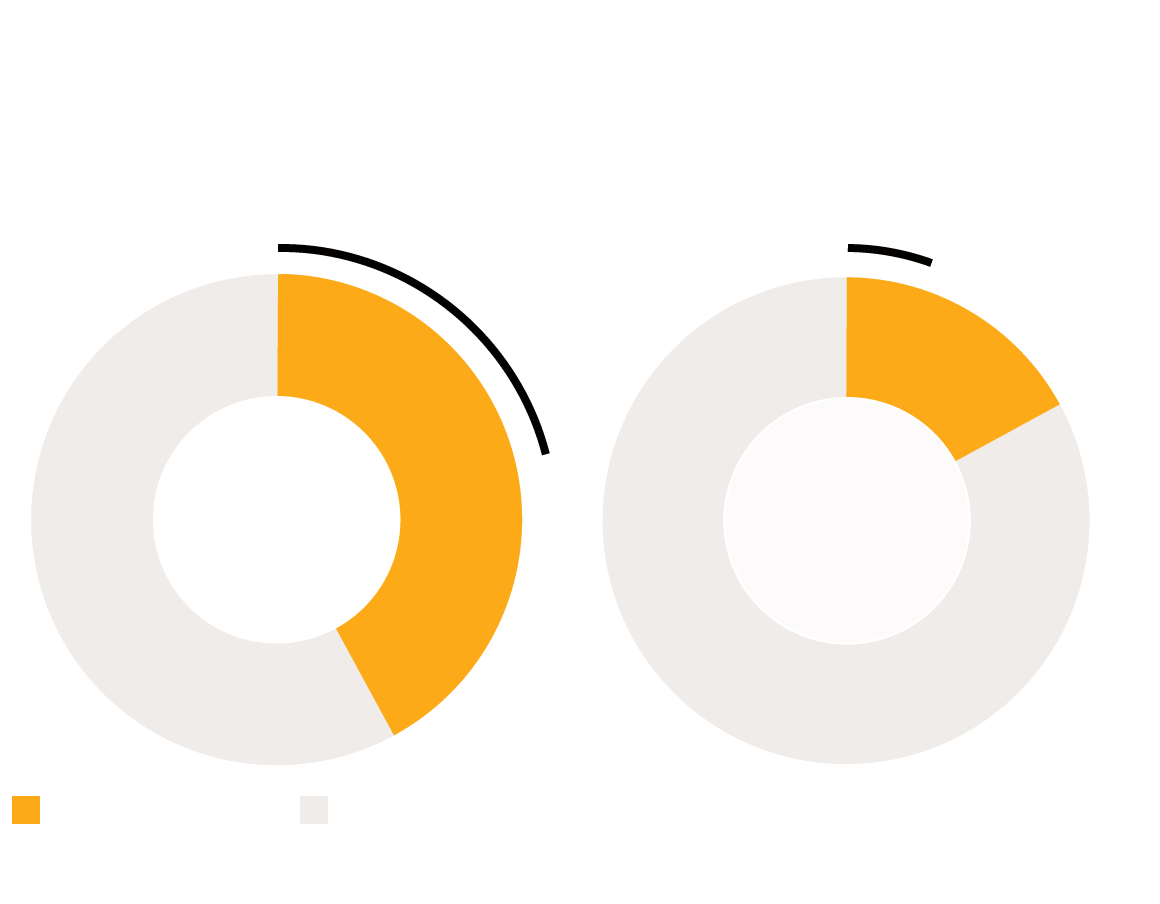
Black People Denied Funds More Often Despite Being 2.5x
More Likely to be Victims of Homicide or Shooting
Percentage of victims of homicides and shootings that were granted or denied
funds by the Oklahoma Victims Fund
50% denied funds
32% denied funds
17%
42%
Black Victims
White Victims
Homicide/Shooting
Other Crime
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or “withdrawn” statuses were eliminated from analysis. The category
“homicide/shooting” is made up of any crimes that contained “shooting with intent to kill,” or “homicide” in their descriptions.
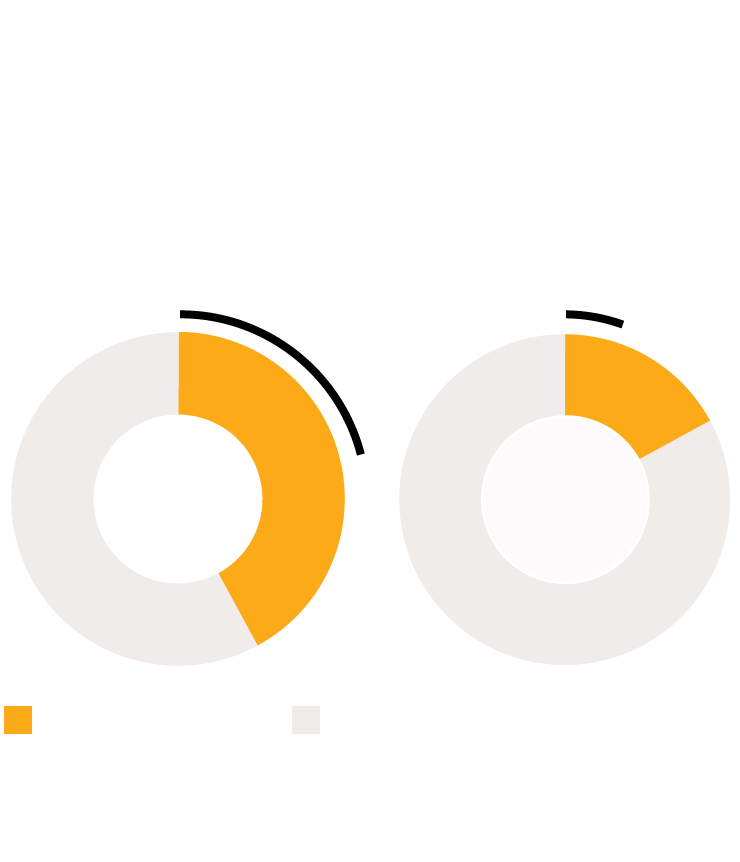
Black People Denied Funds More Often
Despite Being 2.5x More Likely to be
Victims of Homicide or Shooting
Percentage of victims of homicides and shootings that
were granted or denied funds by the Oklahoma Victims
Fund
50% denied funds
32% denied funds
17%
42%
Black Victims
White Victims
Homicide/Shooting
Other Crime
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or “withdrawn” statuses
were eliminated from analysis. The category “homicide/shooting” is made up of
any crimes that contained “shooting with intent to kill,” or “homicide” in
their descriptions.
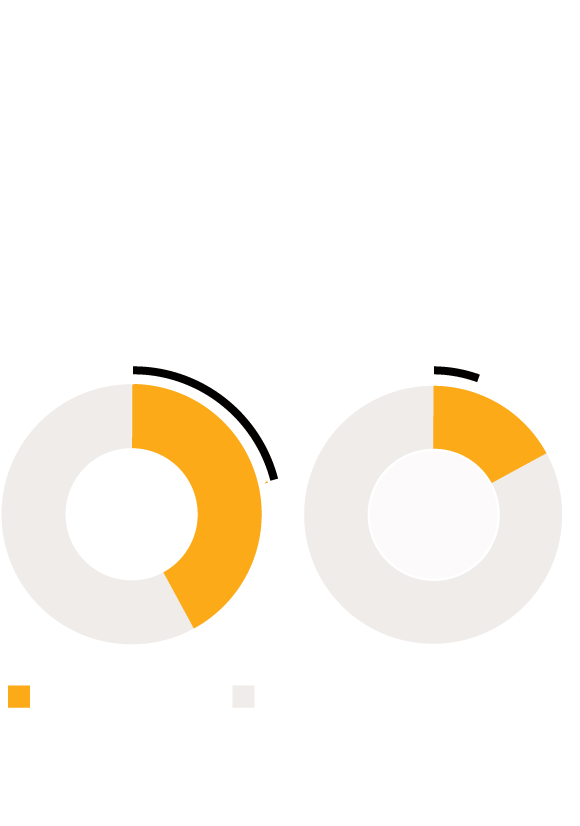
Black People Denied Funds
More Often Despite Being 2.5x
More Likely to be Victims of
Homicide or Shooting
Percentage of victims of homicides and
shootings that were granted or denied
funds by the Oklahoma Victims Fund
50% denied funds
32% denied funds
17%
42%
Black Victims
White Victims
Homicide/Shooting
Other Crime
Notes: Crimes with “pending,” “continued,” “rescind” or “withdrawn”
statuses were eliminated from analysis. The category
“homicide/shooting” is made up of any crimes that contained
“shooting with intent to kill,” or “homicide” in their descriptions.
When looking into reasons why victims were denied funds, Black men, like Tiras, were denied because of “contributory conduct” 43% of the time compared to 31% of white men and 8% of white female victims. More often than not, the people denied funds due to their potential contribution to the crime were victims of homicides or shootings with intent to kill. In fact, when limiting analyses to only these crime types and controlling for other crime factors, Black victims were 1.6 times more likely than white victims to be denied funding due to “contributory conduct,” and male victims of any racial or ethnic background were 4.5 times more likely than female victims to be denied for this reason.
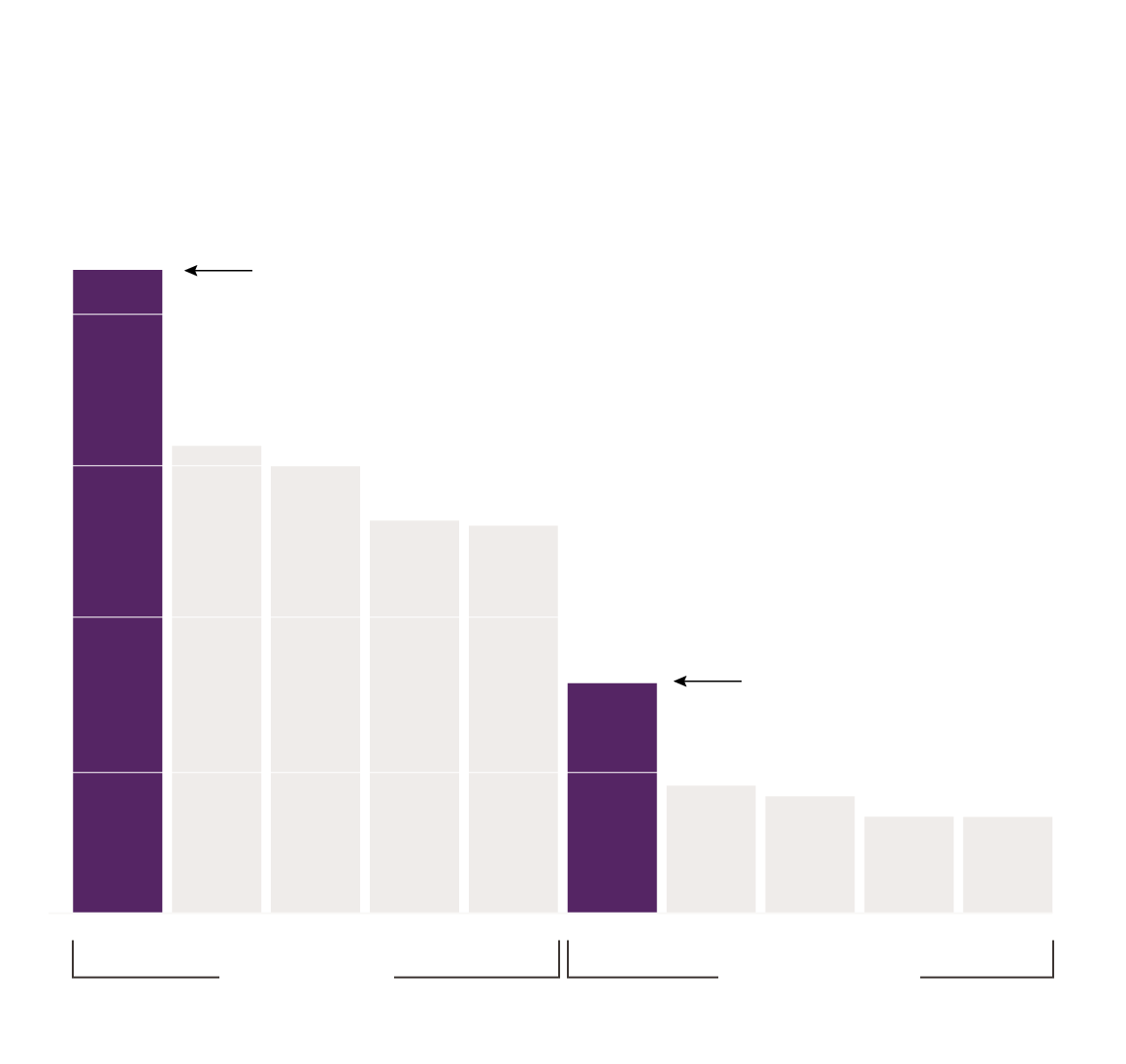
Denial Due to Accused Participation in Crime
Male victims (especially Black male victims) were denied funds due to “contributory
conduct” more often than female victims
50% of denials
43% of denials of funds for
Black men were because of
perceived participation in crime.
40%
30%
20%
Black women were
denied due to “contributory
conduct” almost 2x as often
as white women.
10%
0%
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Male Victims
Female Victims
Notes: Due to small sample sizes, the racial category “Other” consists of Asian/Asian Pacific Islanders, multiple
races, Native Hawaiians and “Other.”
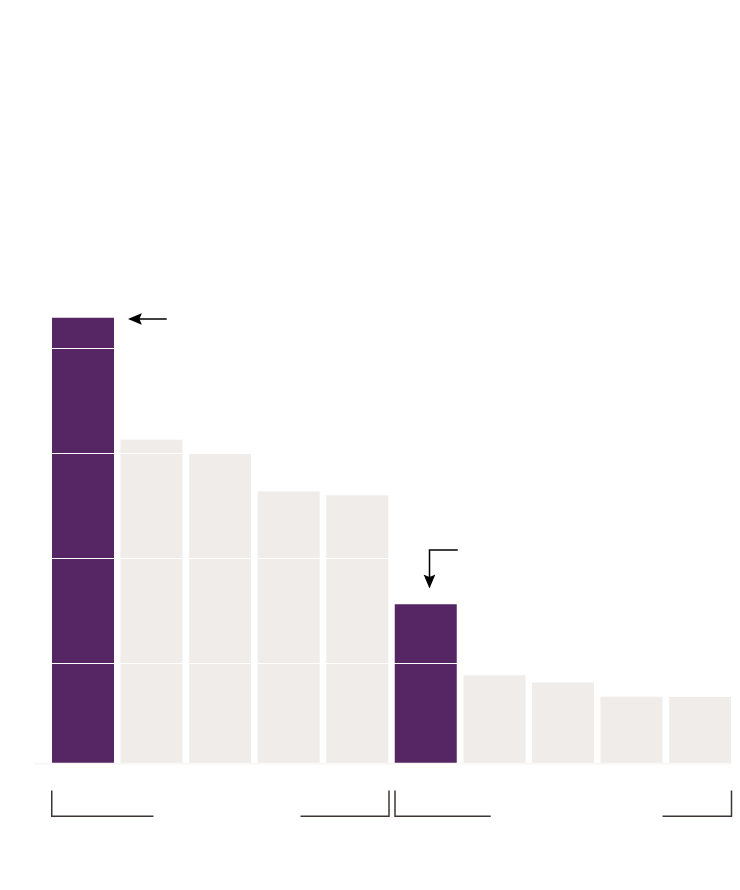
Denial Due to Accused Participation
in Crime
Male victims (especially Black male victims) were
denied funds due to “contributory conduct” more
often than female victims
50% of denials
43% of denials of funds for
Black men were because of
perceived participation in crime.
40%
30%
Black women were denied
due to “contributory
conduct” almost 2x as often
as white women.
20%
10%
0%
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Male Victims
Female Victims
Notes: Due to small sample sizes, the racial category “Other” consists of
Asian/Asian Pacific Islanders, multiple races, Native Hawaiians and “Other.”
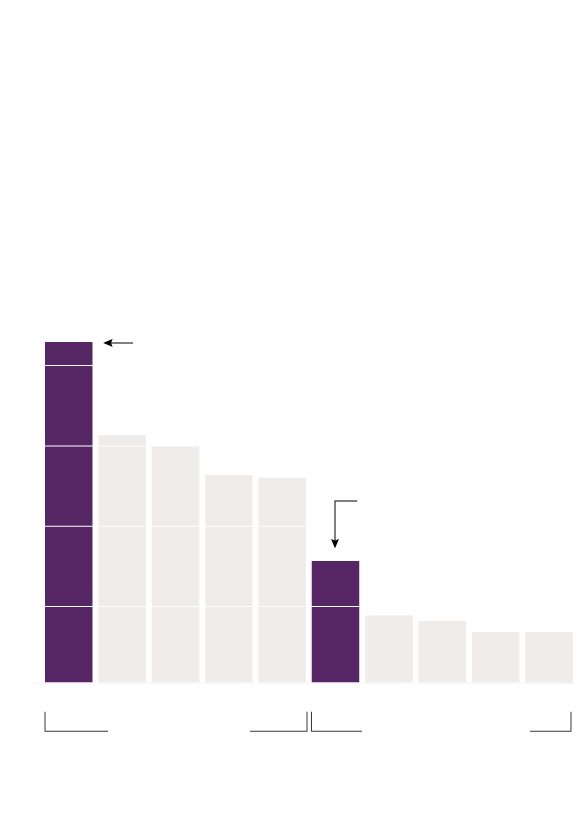
Denial Due to Accused
Participation in Crime
Male victims (especially Black male
victims) were denied funds due to
“contributory conduct” more often than
female victims
50% of denials
43% of denials of funds
for Black men were
because of perceived
participation in crime.
40%
30%
Black women were
denied due to
“contributory conduct”
almost 2x as often as
white women.
20%
10%
0%
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Black
White
Hisp.
Nat. Am.
Other
Male Victims
Female Victims
Notes: Due to small sample sizes, the racial category “Other”
consists of Asian/Asian Pacific Islanders, multiple races, Native
Hawaiians and “Other.”
Victim’s Funds should continue to exist and provide compensation to suffering victims and families, but should take a close look at biases and resulting disparate treatment. To begin, it appears the Council is operating under the assumption that if a person is in any way associated with a gang or even speaks about a gang, they are 100% responsible for their own murder, as was the case with Tiras. At the least, this assumption reflects a blame-the-victim mentality that is not reflected in other contexts. Second, we urge the District Attorneys Council to go back and examine the reasons why contributory negligence is cited at far greater levels for Black people than for white people. District Attorneys should be representing the entire county and the Victims Compensation Fund should be available for all victims in Oklahoma.
Via RSSMix.com Mix ID 8247012 http://www.rssmix.com/
Comments
Post a Comment